Saudi Arabia’s First Quantum Computer: A New Era for Science, Industry, and the Middle East
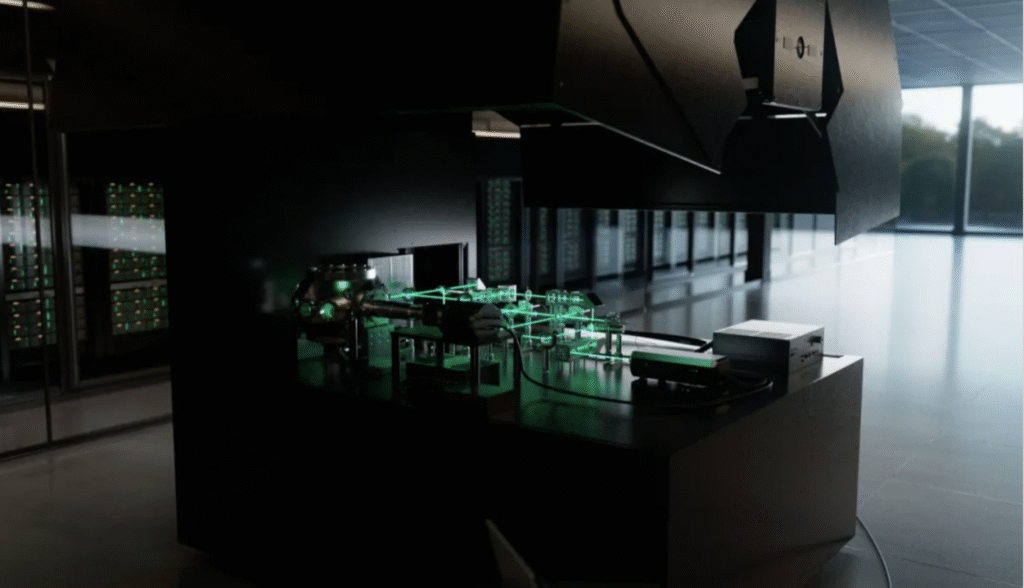
Quantum computing is one of the most transformative technological fields of our era. It promises to solve problems that conventional computers would struggle with for centuries, especially in optimization, climate science, energy, medicine, and cybersecurity. In late 2025, Saudi Arabia became the first country in the Middle East to deploy a fully operational industrial quantum computer. This step marks a significant shift for the Kingdom, placing it among the world’s early adopters of advanced quantum technologies.
TLDR — Quick Summary
- Saudi Arabia deployed its first industrial quantum computer, built with Pasqal and installed at Aramco’s Dhahran data center.
- The system uses neutral-atom qubits, offering scalability, longer coherence, and strong performance for real-world industrial tasks.
- Primary use cases include energy optimization, climate modeling, post-quantum cybersecurity, healthcare simulations, and AI acceleration.
- The initiative positions the Kingdom as a regional quantum hub, supporting Vision 2030 with talent development, startups, and advanced research.
Why the Saudi Arabia’s quantum computer Deployment Matters
Saudi Arabia’s first quantum computer was developed through a partnership between Aramco and Pasqal, a global leader in neutral atom quantum systems. The system was installed in Aramco’s data center in Dhahran. Unlike academic lab prototypes, the machine was built for real industrial applications, particularly in the energy and sustainability sectors.
This deployment is not a standalone event. It builds on several years of investment, ecosystem development, research programs, government initiatives, and technology partnerships. The launch aligns with Vision 2030, which aims to diversify the economy beyond oil and push the country into high impact technology sectors.
How the Saudi Arabia’s Quantum Computer Works
The system developed by Pasqal uses neutral atom quantum technology. Atoms are arranged into programmable two dimensional patterns and manipulated using precisely controlled lasers. This approach offers significant advantages:
- Scalability – More qubits can be added without drastically increasing hardware complexity.
- Longer coherence times – Atoms maintain quantum states longer than many competing qubit types.
- Flexible architectures – Atoms can be arranged into geometries suited for simulation and optimization.
The platform supports both gate based digital quantum operations and analog quantum computing. That flexibility allows developers to explore a wide range of real-world use cases such as industrial modelling, logistics optimization, and physics-informed machine learning.
Where Quantum Will Be Used
Energy Optimization
Saudi Arabia’s first applications will likely focus on energy sector challenges. Quantum computers can simulate reservoirs, optimize pipeline flow, and accelerate materials analysis for hydrogen, carbon capture, and efficient power systems.
Climate and Environmental Science
Traditional supercomputers struggle with climate models involving millions of variables and nonlinear interactions. Quantum systems can simulate these more efficiently, enabling nations to design better mitigation strategies for extreme weather, water scarcity, and greenhouse gas management.
Cybersecurity and Post Quantum Cryptography
Quantum computing will eventually make some current encryption methods weak. Saudi Arabia is already investing in quantum secure communication, preparing public and private infrastructures for a post quantum security environment.
Healthcare and Drug Discovery
Quantum algorithms can model large molecules, protein folding, and chemical interactions with precision. This capability could accelerate drug development, enable personalized medicine, and improve biomedical modeling.
National Security and Strategic Intelligence
Quantum technology enhances simulation, surveillance modeling, and secure communications. Saudi Arabia views this infrastructure as a pillar of digital sovereignty.
The Strategic Impact on the Middle East
Saudi Arabia is positioning itself as a regional quantum hub. The Kingdom’s strategy isn’t just to own a quantum computer, but to build an innovation ecosystem:
education, R&D pipelines, commercial applications, and startup acceleration.
Saudi initiatives emphasize practical and commercially relevant outcomes. Instead of prioritizing purely academic experiments, the Kingdom is using quantum tools to solve energy, supply chain, and climate problems that impact real infrastructure. This approach attracts private investment seeking tangible returns instead of theoretical research.
Universities have launched quantum research tracks, graduate programs, and dedicated lab facilities. Startups exploring algorithms, data analytics, encryption, and materials science receive support through funding initiatives and international partnerships.
The message is clear: Quantum computing is not a curiosity—it is a pillar of national competitiveness.
Challenges Ahead
Saudi Arabia’s progress also faces major obstacles.
Talent Shortage
The country has a limited pool of quantum engineers, physicists, and AI researchers. Saudi Arabia must compete with nations across North America, Europe, and Asia to attract high skill talent.
Infrastructure Limitations
Specialized quantum labs, foundries, and testing facilities remain scarce. Building them requires sustained investment and long term planning.
Transition to Quantum Safe Systems
Industrial sectors will need to adopt post quantum encryption. Banks, telecom companies, and government institutions rely heavily on systems that will not withstand future quantum attacks. Migrating to quantum resistant standards is slow and technically complex.
Energy & Maintenance Requirements
Quantum systems demand controlled environments:
cooling, vibration isolation, laser systems, and precise calibration. Even neutral atom approaches require highly specialized technical management.
Regulatory & Ethical Considerations
Quantum computing introduces debates around data security, weaponization, IP ownership, and international competition. New policy frameworks will be required to manage responsible innovation.
How Saudi’s Approach Differs From Other Countries
Global quantum leadership is currently dominated by the U.S., China, and Europe. These regions rely heavily on federal funding, academic research, and long horizon development.
Saudi Arabia is taking a different approach:
Industrial first quantum deployment.
Instead of beginning with universities, the Kingdom started with a major industry installation. This mirrors Saudi’s approach in artificial intelligence, semiconductors, and cloud computing, where it leverages large organizations to accelerate early adoption.
If successful, this model may help quantum applications reach commercial utility faster than traditional, research led ecosystems.
Impact on Citizens and Industry
Saudi Arabia’s first quantum computer will influence the country for years to come.
New Careers and Research Fields
Pasqal and Aramco will train engineers, build specialized teams, and integrate with universities. Researchers will access local quantum hardware instead of relying on international facilities.
Economic Opportunities
Quantum creates new markets:
algorithm design, quantum as a service, optimization consulting, and simulation based R&D. These attract startups, investors, and global partners.
Education Expansion
Universities are launching quantum technology and engineering programs. Students will be prepared early through physics, mathematics, cryptography, and AI pathways.
Startup Ecosystem Growth
Saudi initiatives support founders in energy tech, healthcare, climate technology, and industrial AI. Quantum computing enables these sectors to model complex systems in ways impossible before.
Looking to the Future
Saudi Arabia plans to expand its quantum ecosystem over the coming decades. Key initiatives include:
- Establishing a Quantum Valley technology district
- Building a quantum hardware foundry
- Scaling workforce development from schools to advanced research teams
The country has also designated quantum computing as a national moonshot, aiming to achieve fault tolerant, scalable systems by the mid 2040s.
International partnerships will remain essential. By participating in global standards, strategic alliances, and policy frameworks, Saudi Arabia plans to avoid technological isolation and accelerate its growth.
Conclusion
Saudi Arabia’s first quantum computer is more than a symbolic achievement—it is a turning point. By combining industrial deployment, academic expansion, and international partnerships, the Kingdom is building a foundation for a future where quantum technologies deliver real scientific, economic, and strategic value.
Challenges remain—talent, infrastructure, cost, and global competition—but the Kingdom’s practical, use case driven approach shows serious intent. Quantum computing is no longer happening elsewhere. It is here—and its impact will grow for decades to come.
Read CoinDCX Hack Explained: $44 Million Breach, Timeline, Impact and Future of Crypto Security
FAQs
What is a quantum computer?
A machine that uses quantum physics to solve problems far faster than traditional computers.
Why is Saudi Arabia’s system important?
It is the first industrial quantum computer in the Middle East, focused on real business applications.
Where is it located?
It is installed at Aramco’s facility in Dhahran.
What can it be used for?
Energy optimization, climate modeling, cryptography, healthcare research, and AI development.
Who will benefit from it?
Researchers, startups, universities, government agencies, and industries throughout Saudi Arabia.

